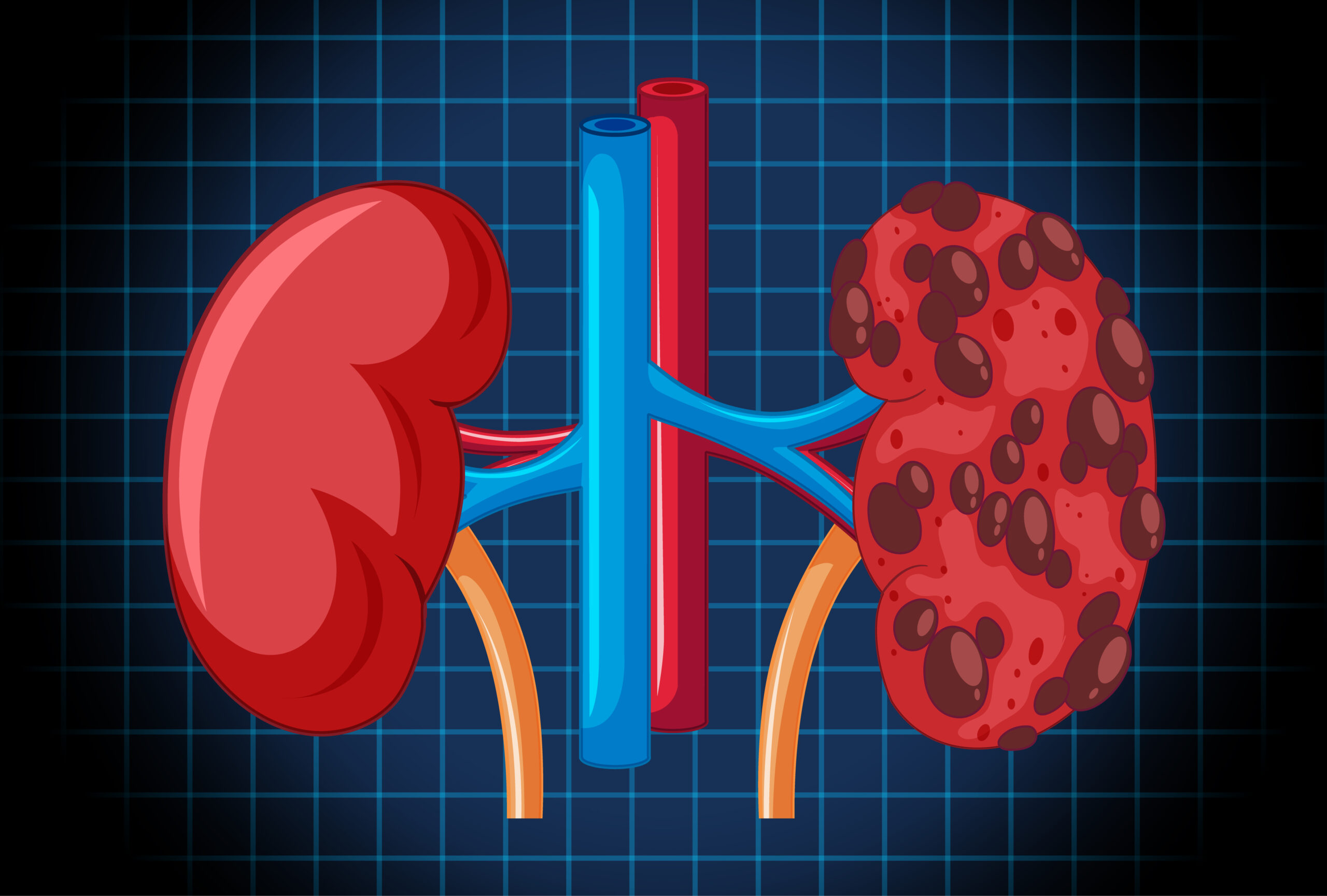
Introduction to Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD)
Polycystic Kidney Disease diagnosis is important for your kidney health. PKD is a condition where many fluid-filled sacs, called cysts, grow in the kidneys. These cysts can make the kidneys larger and may cause them to stop working well over time. Although PKD can run in families, anyone can be affected. Early diagnosis helps manage the disease and protect your health.
Common Symptoms Leading to Diagnosis
Often, people do not notice symptoms in the early stages. However, some signs may suggest you need a kidney health screening. For example, you might experience:
Because these symptoms can be mild, it is important to talk to your doctor if you notice any of them. Early signs of polycystic kidney disease are often missed, so regular check-ups help.
Step-by-Step Diagnostic Process for PKD
Doctors use several steps to diagnose PKD. Each step gives important clues about your kidney health. Here is what you can expect:
1. Family History
First, your doctor will ask about your family. Since PKD often runs in families, knowing if a close relative has the disease helps. If you have a family member with PKD, your risk is higher.
2. Physical Examination
Next, your doctor will check your body. They may feel your abdomen to see if your kidneys are larger than normal. Sometimes, they check your blood pressure as well, since high blood pressure is common in PKD.
3. Blood and Urine Tests
After that, your doctor may order blood and urine tests. These tests check how well your kidneys are working. For example, blood tests can show if waste products are building up. Urine tests can find blood or protein, which may be signs of kidney problems.
4. Imaging Tests
Imaging tests are key for PKD diagnosis. These tests let doctors see your kidneys and look for cysts. Common imaging tests include:
With these tests, doctors can confirm if you have PKD and see how much your kidneys are affected.
Importance of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis of polycystic kidney disease is very important. When PKD is found early, you can take steps to slow down kidney damage. For instance, you can manage your blood pressure, eat a healthy diet, and avoid certain medicines. Early care helps you stay healthier for longer. According to the National Kidney Foundation, early treatment can delay serious kidney problems.
What to Expect During and After Diagnosis
During the diagnosis, you may feel nervous. However, most tests are simple and painless. After your diagnosis, your doctor will explain the results. They will talk about your treatment options and how to care for your kidneys. You may need regular check-ups to watch your kidney health. With the right care, many people with PKD live active lives.
Frequently Asked Questions About PKD Diagnosis
Conclusion
Polycystic Kidney Disease diagnosis is the first step to better kidney health. Early detection helps you and your doctor make the best plan for your future. If you have symptoms or a family history of PKD, do not wait. Consult a nephrologist for personalized advice and early diagnosis of Polycystic Kidney Disease.